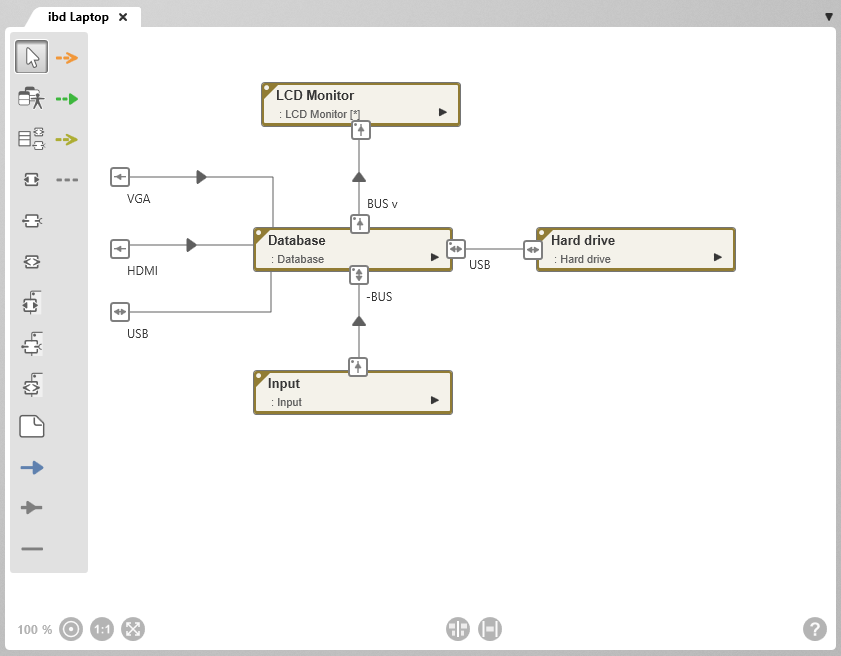
The Internal Block Diagram
An internal block diagram describes the structure and flows within a block. Internal block diagrams provide a simple overview of how the parts of a block interact and what kind of data, information, signals or materials flow in which directions. It represents what happens inside a block.